Overview
The purpose of this portfolio is to document the contributions I have made to the ModuleBook project.
The ModuleBook project is developed by a team of 4 software engineering students as a requirement for the CS2103T module taught at the National University of Singapore (NUS).
ModuleBook is a module tracking and planning application for students of NUS. It allows students to view and track modules, as well as add deadlines and other useful information such as hyperlinks.
Summary of contributions
Major enhancement: added archived modules
-
What it is: Archived modules contain module data from NUSMods, such as the module code, title, description, prerequisites, preclusions and semester data (exam dates and whether the module is offered for the semester).
-
Justification: This feature allows developers to use existing data from NUSMods to perform operations, such as filtering (find command). This feature also allows users to view data from NUSMods.
Major enhancement: added the ability to view modules
-
What it does: Allows users to view an archived module to get more details. Also allows users to view a tracked module to access and modify deadlines and hyperlinks.
-
Justification: This feature enhances the user experience by only displaying details from a single module at any one time. It also minimizes details to be displayed on the module list.
-
Highlights: This feature creates a context for users to perform commands pertaining to a module. For example, a user can specify that they want to add a hyperlink to the module they are viewing without specifying the module in the command.
-
Credits: The view feature is a result of the observation of many popular applications on the market, such as Telegram, Discord, Outlook.
Minor enhancement: Refactor module list to display archived modules and tracked modules together, with tracked modules overriding the referenced archived modules. (Pull request #142)
Code contributed: Link to RepoSense for functional and test code
Other contributions:
-
Project management:
-
Managed releases
v1.1-v1.4(Release page) -
Managed milestones
v1.1-v1.4on Github (Milestone page) -
Managed user stories on Github (User stories page)
-
-
Morphing from AddressBook to ModuleBook:
-
Documentation:
-
Update website style to center images and image titles (Pull request #164)
-
-
Community:
-
Tools:
-
Setup project repo with CI tools: travis and coveralls
-
Setup project repo with netlify for website deployment preview
-
Contributions to the User Guide
Given below are sections I contributed to the User Guide. They showcase my ability to write documentation targeting end-users. |
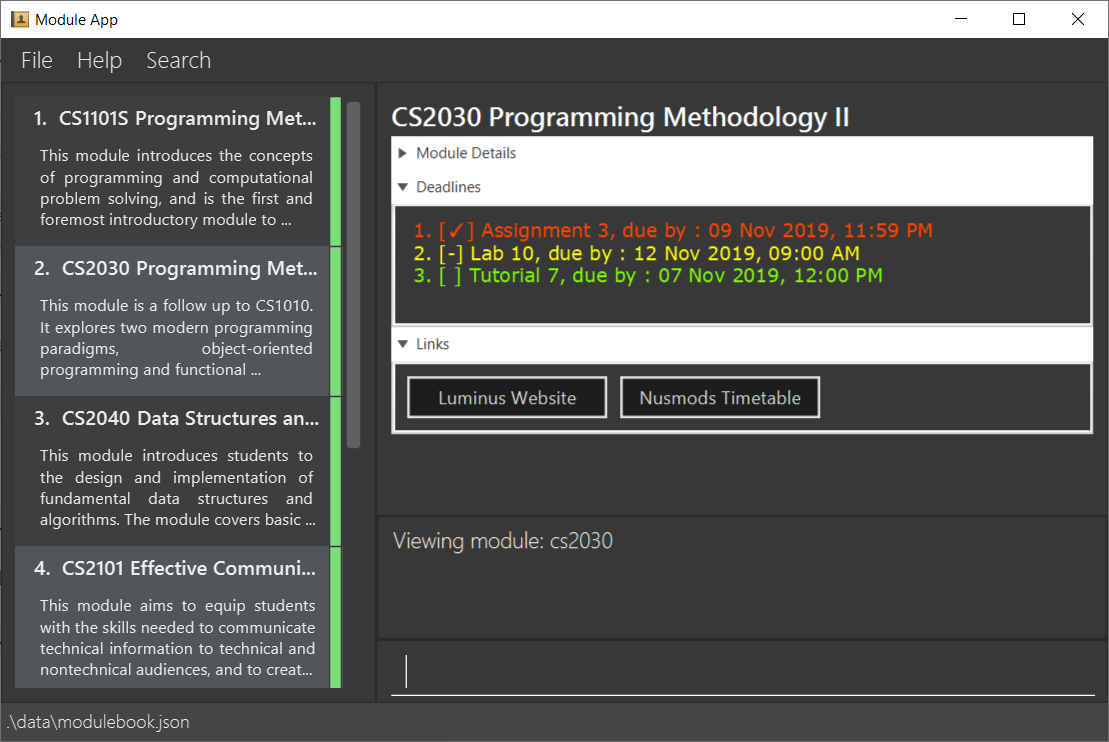
Viewing a module: view
Method 1: Typing the command
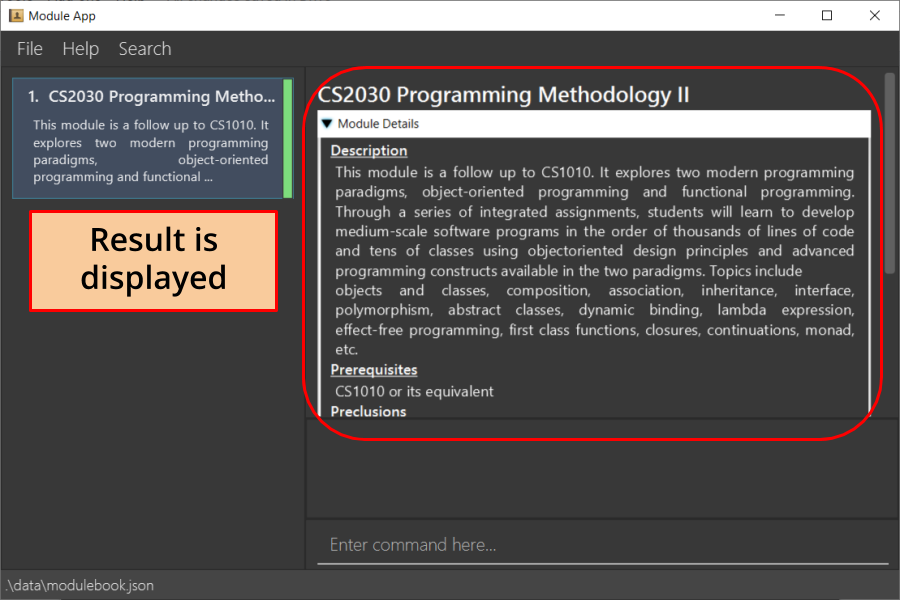
Views a module and enters the module view. Can be a tracked module or an archived module.
Format: view <MODULE_CODE>
Example: view cs1231
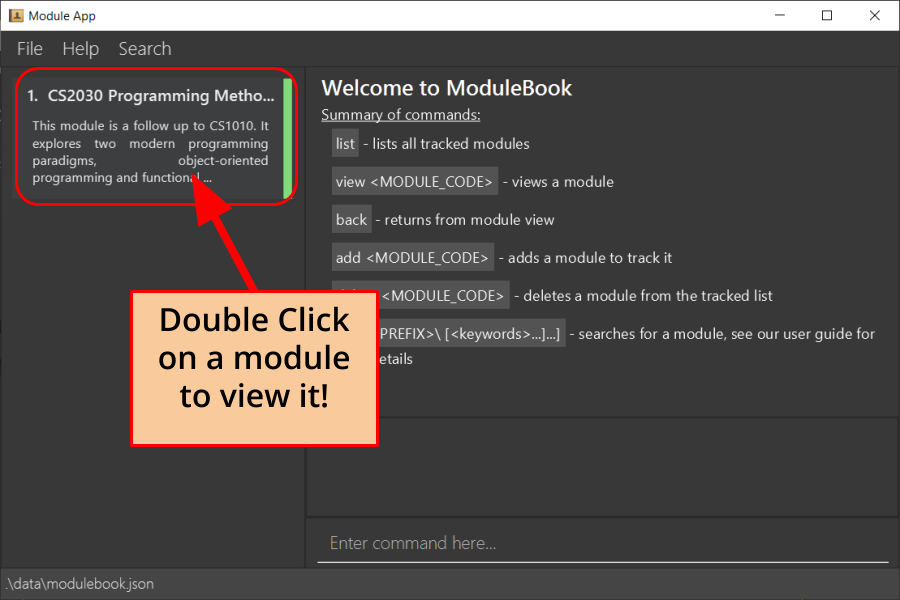
Method 2: Double clicking on the module in the list
Alternatively, you may simply view the module by double clicking on the module in the module list.
Contributions to the Developer Guide
Given below are sections I contributed to the Developer Guide. They showcase my ability to write technical documentation and the technical depth of my contributions to the project. |
Module View Feature
The module view feature allows users to view a module to access extra information about the module. The user can view (and unview) a module using the view (and back) commands.
Implementation
The module view feature is facilitated by displayedModule in ModelManager. The following describes how the displayedModule is modified and read to the Ui.
-
The user enters a view command in the
Ui. -
LogicManagerparses the user input, constructs and executes theViewCommand. -
The
ViewCommandattempts to find the matching module from the list of Tracked Modules, else it attempts to find the matching module from the list of Archived Modules, else it throws an exception. -
The
ViewCommandsets thedisplayedModulein theModeland returns theCommandResultto theLogicManager. -
The
LogicManagerreturns theCommandResultto theUi. -
The
Uigets thedisplayedModulefromLogicManagerand updates the Ui to display the module.
The following sequence diagram shows how the module view feature is executed.
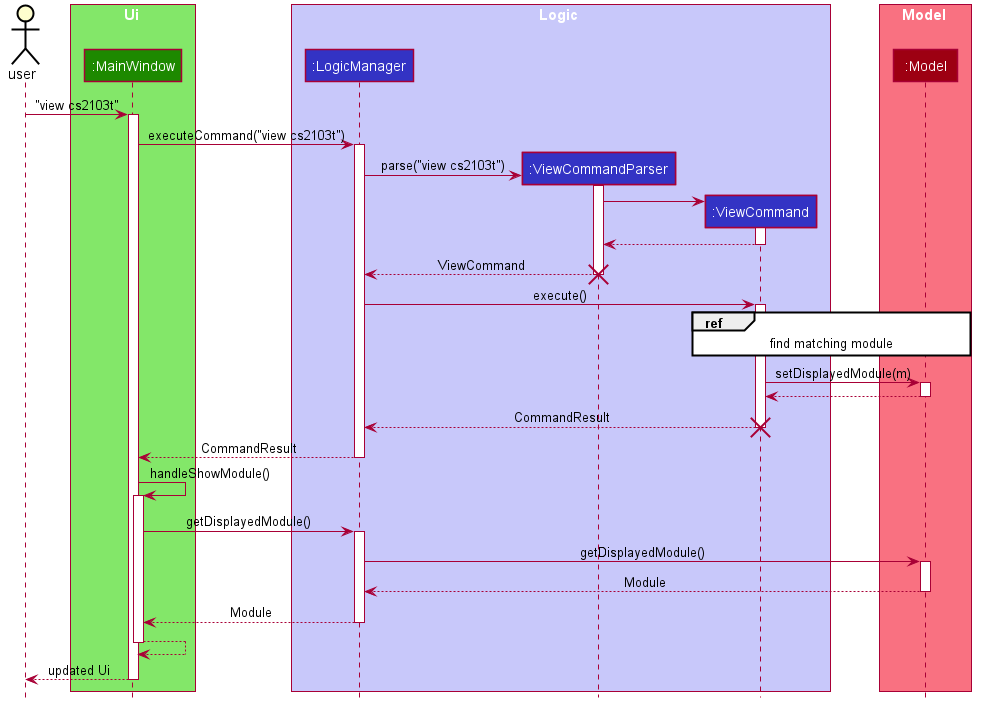
The BackCommand mostly follows the same sequence as described above, except that it does not need to find any module, and sets the displayed module to null.
|
The following activity diagram describes the process of finding a matching module to display.
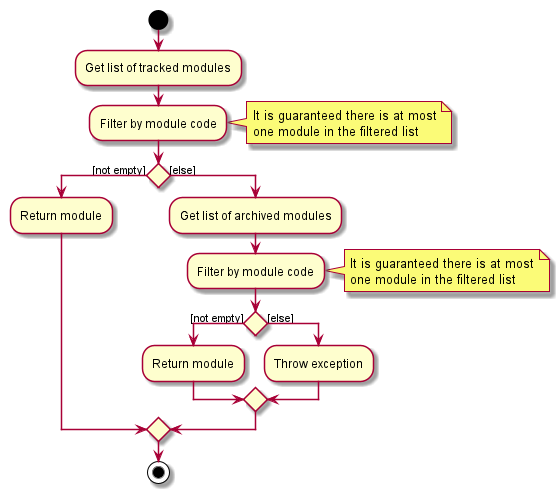
Design Considerations
Updating the Ui
Current Implementation: New field in the CommandResult that the Ui will check to determine if it needs to update.
Pros:
-
Simple and easy to control what command updates the Ui.
Cons:
-
More difficult to maintain over the course of the project. New Ui elements require new fields to update the Ui.
Alternate Implementation: Every command updates the Ui.
Pros:
-
Maintainance free.
Cons:
-
Potentially inefficient.
-
Possible side effects from certain commands.
[Proposed] Marking modules as completed, ongoing or planned
Users can mark modules as
Implementation
The tracked module will have 2 new fields: moduleStatus and semesterTimestamp.
The moduleStatus will be an enumeration of:
-
completed , -
ongoing and -
planned .
The semesterTimestamp will be a combination of:
-
an academic year
-
In NUS, the academic year representation is prefixed with "AY", followed by the last 2 digits of the starting year, and the last 2 digits of the ending year
-
e.g. AY1920, AY2021
-
-
a semester
-
In NUS, there are a total of 4 semesters. Semester 1, Semester 2, Special Term 1 (ST1) and Special Term 2 (ST2).
-
e.g. 1, 2, ST1, ST2
-
The user will be free to modify the moduleStatus and the semesterTimestamp. The following class diagram will illustrate the above implementation.
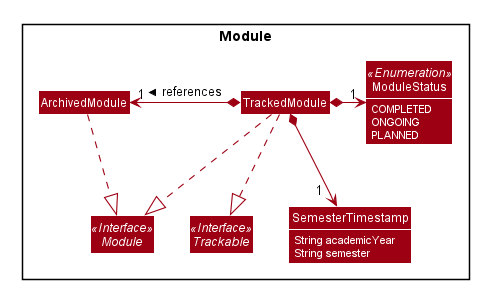
Possible Extensions
With the new data, users may be able to easier manage their tracked modules and gleam useful information.
-
Completed modules will be hidden from the module list, but still viewable through alistallcommand (proposed command) and accessible through theviewcommand. -
Completed modules andongoing modules can be used to determine if a user fulfil the requirements for theirplanned modules .